Incredible Insights into Web Application Architecture: Essential Components and Layers
Introduction
Web application architecture is fundamental to the efficient operation and user experience of web apps. This guide explores the essential components and layers, detailing both visible elements and backend operations that ensure applications run smoothly and effectively.
UI/UX Components: The Face of Web Applications
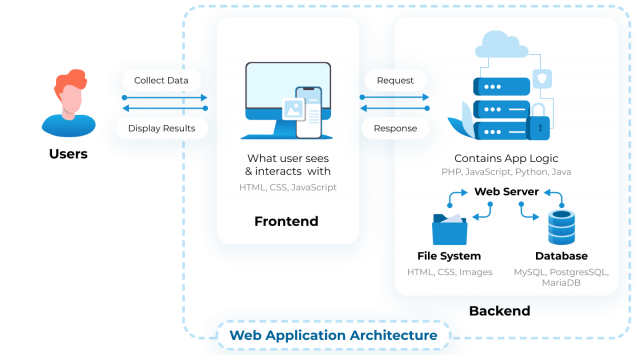
Web applications are composed of two primary types of components: UI/UX components and architectural components. The UI/UX components encompass all the elements that users interact with directly. This includes everything from the layouts and notifications to the dashboards they navigate. These components are crucial as they define the user's experience, dictating the ease with which users can interact with the various functionalities of the application.
The client side of a web application is what the user sees and interacts with. It is primarily built using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, forming the frontend of the application. This part of the web app is responsible for presenting information, receiving user inputs, and providing a dynamic interaction through visual elements.
Architectural Components: The Backbone of Functionality
Moving beyond the surface, the architectural components of a web application consist of the server side and the databases that support the business logic and data storage needs of the application. Common programming languages used for server-side development include PHP, Java, Ruby on Rails, Python, and Node.js.
The server side is split into several layers, each with a specific function:
- Presentation Layer (PL): This is the layer that users interact with. It includes all the interface elements and processes that help users navigate the application.
- Business Logic Layer (BLL): Here lies the core functionality of the application, where data exchange and processing of business rules occur.
- Data Service Layer (DSL): This layer acts as a mediator between the business logic layer and the presentation layer, facilitating the flow of data.
- Data Access Layer (DAL): Focused on data retrieval and management, this layer handles operations such as create, read, update, and delete (CRUD).
Each of these layers plays a pivotal role in the seamless operation of web applications, ensuring that user requests are processed efficiently and that the application remains robust and scalable.
Scalability and Integration
An essential aspect of web application architecture is scalability. A well-designed architecture allows for the easy addition of more servers and databases to handle increased load. This capability ensures that the application can grow and evolve without sacrificing performance or user experience.
In summary, understanding the components and layers of web application architecture is crucial for developers and stakeholders involved in creating or managing web apps. By ensuring each layer operates optimally and integrates seamlessly with the others, organizations can deliver powerful, user-friendly applications that stand the test of time.